3273 字
16 分钟
⛓️吃透LinkedList与链表的终极指南

🌟 引言
在Java集合框架中,LinkedList和ArrayList是最常用的两种列表结构。它们各有优劣,适用于不同的场景。本文将带你深入探索LinkedList的底层实现——链表,并通过丰富的代码示例和对比分析,帮助你全面掌握其特性和应用场景。

📚 1. ArrayList的缺陷
ArrayList底层基于动态数组实现,虽然支持高效的随机访问(时间复杂度为==O(1)==),但在任意位置插入或删除元素时,需要搬移后续元素,导致时间复杂度为==O(n)==。例如:
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(1); // 添加到末尾,O(1)list.add(0, 0); // 插入到头部,O(n)缺陷总结:
- 插入/删除效率低(尤其是头部或中间位置)。
- 扩容时需要拷贝数据,额外开销大。
🔗 2. 链表:LinkedList的底层结构W
2.1 链表的概念
链表是一种物理存储非连续的数据结构,通过节点的引用(指针)实现逻辑上的连续性。
 特点:
特点:
- 节点包含数据域和指针域。
- 物理上不连续,逻辑上连续。
2.2 链表的分类
链表有多种结构组合,常见的两种:
-
无头单向非循环链表:结构简单,常用于面试题。
-
无头双向循环链表:Java中
LinkedList的底层实现。
双向链表节点定义:
class Node { int val; Node prev; Node next;}⚙️ 3. LinkedList的模拟实现
以下是一个简化版的无头单链表实现:
/*关于LinkedList的实现练习,只实现String属性*/
//通过这个类来表示一个链表的单链表节点,如果是双链表还需要一个prev/*关于LinkedList的实现练习,只实现String属性*/
//通过这个类来表示一个链表的单链表节点,如果是双链表还需要一个prevclass Node{ //节点保存的值,为了练习方便把属性设置为public public String value; //节点的下一个元素 public Node next;
//创建构造方法进行初始化 public Node(String value){ this.value = value; this.next = null; }
}
public class MyLinkedList {
//表示链表的头节点 //由于此处不考虑傀儡节点,所以当head为空时,表示为一个空链表 private Node head = null; //不像顺序表搞一个size表示有效元素的区间
//尾插 public void addLast(String value){ //如果head为null,直接让它指向新节点 if(head == null){ Node newNode = new Node(value); head = newNode; return;
} //思路:先找到尾巴 //先把尾巴指向head节点,一直遍历往下找 Node tail = head;
for (; tail != null; tail = tail.next){ if(tail.next == null){ break; } } //通过上述循环,循环结束之后,此时的tail指向尾巴了 //此时就创建新的节点,让尾节点的next指向newNode Node newNode = new Node(value); tail.next = newNode; //再把newNode的节点指向null,由于在构造方法中中已经做了这件事,不写也没关系 newNode.next = null; }
//头插 public void addFirst(String value){ //根据刚才value的值,创建一个节点 Node newNode = new Node(value); //把新的节点放到头位置做两件事: //1.把新节点的next指向原来的头节点 newNode.next = head; //2.让head指向新节点 head = newNode;
}
//指定位置插入 public void add(int index, String value){
//1.先进行合法性检查 if(index < 0 || index > size()){ //index == size时相当于尾插,属于合法情况 throw new RuntimeException("Index out of bounds"); }
//2.针对头插特殊处理 if(index == 0){ addFirst(value); return; }
//3.根据当前value值,去新建一个节点 Node newNode = new Node(value);
//4.找到index要插入的位置的上一个节点 // 由于当前的链表是单向链表,每个节点,只能找到next // 插入新节点需要修改前一个节点的next值 // 前一个节点的下标应该是index-1 Node prev = head; for (int i = 0; i < index-1; i++) { prev = prev.next; }
//5.通过上述循环,就让prev指向index-1的位置 newNode.next = prev.next; prev.next = newNode;
}
//虽然没有size但是我们可以现成写一个size() //但是这样的过程时间复杂度为O(N) public int size(){ int size = 0;
for (Node current = head;current != null; current = current.next){ size++; } return size; }
//实现判定某个元素是否在链表中包含 public Boolean contains(String value){ for (Node current = head; current != null; current = current.next){ if(current.value.equals(value)){ return true; } } return false; }
//实现搜寻某个元素的下标 public int indexOf(String value){ int index = 0; for(Node current = head; current != null; current = current.next){ if(current.value.equals(value)){ return index; } index++; } return -1; }
//实现删除链表中的某个元素操作(指定下标) public void remove(int index){ if(index < 0 || index >= size()){ throw new RuntimeException("Index out of bounds"); }
// //自己实现的想法// //判断下标为0// if(index == 0){// head = head.next;// }// int lastIndex = 0;// for (Node prev = head; prev != null; prev = prev.next){// Node toRemove = prev.next;// if( lastIndex == index-1){// prev.next =toRemove.next;// }// lastIndex++;// }
//其他实现做法 //1.这对特殊情况处理 if(index == 0){ head = head.next; return; } //2.找到被删除元素的前一个节点 Node prev = head; for (int i = 0; i < index-1; i++) { prev = prev.next; } //3.循环结束,prev就指向待删除元素的上一个节点 Node toRemove = prev.next; //4.进行删除操作 prev.next = toRemove.next;
} //实现删除链表中的某个元素操作(指定值) public void remove(String value){ //1.先找到元素所在下标 int index = indexOf(value); if(index == -1){ System.out.println("所删除元素不存在"); return; } remove(index);
}
//实现清空链表所有元素 public void clear(){ //直接修改head,head指向原来的Node对象都没有引用指向了,都会被gc回收 head = null; }
//重写toString通过这个方法去遍历链表,构成一个字符串,方便打印 @Override public String toString() { //遍历的时候,需要从头结点开始,进行一个元素一个元素的打印 StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder(); str.append("[");
for (Node current = head;current != null;current = current.next){ if(current.next != null){ str.append(current.value); str.append(","); }else { str.append(current.value); } } str.append("]"); return str.toString(); }
//----------------------------------------------------------
//头插测试 public static void test1(MyLinkedList list){ list.addFirst("A"); list.addFirst("B"); list.addFirst("C"); System.out.println(list); }
//尾插测试 public static void test2(MyLinkedList list){ list.addLast("A"); list.addLast("B"); list.addLast("C"); list.addLast("D"); list.addLast("E"); System.out.println(list); }
//指定位置插入测试 public static void test3(MyLinkedList list){
list.add(0, "a"); list.add(1, "b"); list.add(2, "c"); list.add(3, "d"); list.add(0, "000"); System.out.println(list); }
//查找元素是否存在以及查找元素下标测试 public static void test4(MyLinkedList list){ System.out.println(list.contains("c")); System.out.println(list.contains("000")); System.out.println(list.contains("e")); System.out.println(list.indexOf("c")); System.out.println(list.indexOf("000")); System.out.println(list.indexOf("e")); }
//删除元素测试 public static void test5(MyLinkedList list){ list.remove(0); list.remove(2); System.out.println(list);// list.remove(100); list.remove("b"); System.out.println(list); list.remove("666"); }
//清空链表元素测试 public static void test6(MyLinkedList list){ list.clear(); System.out.println(list); }
//主方法 public static void main(String[] args) { MyLinkedList list = new MyLinkedList();// test1(list); MyLinkedList list2 = new MyLinkedList(); test2(list2);// test3(list2);// test4(list2);// test5(list2); test6(list2); MyLinkedList list3 = new MyLinkedList(); //空链表测试// test4(list3); }}以下是一个简化版的双向链表实现:
//实现双向链表public class MyDLinkedList { //此处创建一个双向链表节点类,由于在这个包中已经存在Node这个类,因此我们创建静态内部类 //用静态是为了不让Node依赖MyDLinkedList的this static class Node { public String value; public Node next = null; public Node prev = null; public Node(String value) { this.value = value; } } //表示整个链表,此处不引入傀儡节点,用null表示空链表 private Node head = null; //为了后续方便去实现尾插操作 private Node tail = null;
//---------------------------------------- //实现链表一些核心操作
//计算链表长度 public int size() { int size = 0; for (Node current = head; current != null; current = current.next) { size++; } return size; }
//头插 public void addFirst(String value) { Node newNode = new Node(value); //链表为空 if(head == null) { head = newNode; tail = newNode; }//链表不空 else { //1.先让新节点和原来的头节点建立关联 newNode.next = head; head.prev = newNode; head = newNode;
}
}
//尾插 public void addLast(String value) { Node newNode = new Node(value); //判断链表为空 if(head == null) { head = newNode; tail = newNode; } //判断链表不为空 else { tail.next = newNode; newNode.prev = tail; tail = newNode; } }
//在中间位置任意插入 public void add(int index, String value) { int size = size(); //避免每次使用都去重新遍历,提高效率 if (index <0 || index > size){ throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: " + index + ", Size: " + size); } if(index == 0) { addFirst(value); return; } if (index == size) { addLast(value); return; } //创建一个prev,指向index上一个节点的位置 Node prev = head; for (int i = 0; i < index-1; i++) { prev = prev.next; } //创建一个next,指向index下一个节点的位置 Node next = prev.next;
//在创建一个插入节点 Node newNode = new Node(value); prev.next = newNode; newNode.prev = prev; newNode.next = next; next.prev = newNode;
} //实现contains方法 public boolean contains(String value) { Node current = head; for (; current != null; current = current.next) { if (current.value.equals(value)) { return true; } } return false; }
//实现indexOf public int indexOf(String value) { Node current = head; int index = 0; for (; current != null; current = current.next) { if (current.value.equals(value)) { return index; } index++; } return -1; }
//删除头部元素 public String removeFirst() { if(head == null) { return null; } String value = head.value; if(head.next != null) { head = head.next; head.prev = null; }else { head = null; } return value;
}
//删除尾部 public String removeLast() { if(head == null) { return null; } String value = tail.value; if(head.next == null) { head = null; tail = null; return value; } tail = tail.prev; tail.next = null; return value; }
//根据索引进行删除 public String remove(int index) { int size = size(); if(index < 0 || index >= size) { throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: " + index + ", Size: " + size()); } //特殊处理 if(index == 0) { return removeFirst(); } if(index == size - 1) { return removeLast(); } Node prev = head; for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) { prev = prev.next; } Node toRemove = prev.next; Node next = toRemove.next; prev.next = next; next.prev = prev; return toRemove.value;
}
//指定值删除 public String remove(String value) { if(head == null) { return null; } if (head.value.equals(value)) { return removeFirst(); } if(tail.value.equals(value)) { return removeLast(); } //遍历链表找到待删除元素位置 String val = null; Node toRemove = head; for(; toRemove != null; toRemove = toRemove.next) { if (toRemove.value.equals(value)) { val = toRemove.value; break; } } if (toRemove == null) { return null; } //真正进行删除 Node next = toRemove.next; Node prev = toRemove.prev; prev.next = next; next.prev = prev;
return val; }
//重写toString @Override public String toString() { StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); Node current = head; stringBuilder.append("["); while(current != null) { if (current.next != null) { stringBuilder.append(current.value); stringBuilder.append(","); } else { stringBuilder.append(current.value); } current = current.next; } stringBuilder.append("]"); return stringBuilder.toString(); }
//------------------------------------------------------------------- private void test1(MyDLinkedList list) { list.addFirst("a"); list.addFirst("b"); list.addFirst("c"); System.out.println(list); }
private void test2(MyDLinkedList list) { list.addLast("a"); list.addLast("b"); list.addLast("c"); System.out.println(list); }
private void test3(MyDLinkedList list) { list.add(0, "1"); list.add(1, "2"); list.add(2, "3"); System.out.println(list); }
private void test4(MyDLinkedList list) { System.out.println(list.contains("1")); System.out.println(list.contains("10")); System.out.println(list.indexOf("2")); System.out.println(list.indexOf("10")); }
private void test5(MyDLinkedList list) {
//测试头删 System.out.println(list.removeFirst()); System.out.println(list.removeFirst()); System.out.println(list.removeFirst()); System.out.println(list);
}
private void test6(MyDLinkedList list) { System.out.println(list.removeLast()); System.out.println(list.removeLast()); System.out.println(list.removeLast()); System.out.println(list); }
private void test7(MyDLinkedList list) { System.out.println(list.remove(1)); System.out.println(list.remove(1)); System.out.println(list.remove(0)); System.out.println(list); }
private void test8(MyDLinkedList list) { System.out.println(list.remove("1")); System.out.println(list.remove("3")); System.out.println(list.remove("10")); System.out.println(list); }
//主程序逻辑 public static void main(String[] args) { MyDLinkedList list = new MyDLinkedList();// list.test1(list);// list.test2(list); list.test3(list);// list.test4(list);// list.test5(list);// list.test6(list);// list.test7(list); list.test8(list); }
}🛠️ 4. LinkedList的使用
4.1 Java集合框架部分:LinkedList继承体系(思维导图)
flowchart TD
A[Iterable] --> B[Collection]
B --> C[List]
B --> D[Queue]
C --> E[LinkedList]
D --> E
E --> F[Deque]
E --> G[AbstractSequentialList]
G --> H[AbstractList]
E --> I[Serializable]
E --> J[Cloneable]
4.2 常用方法
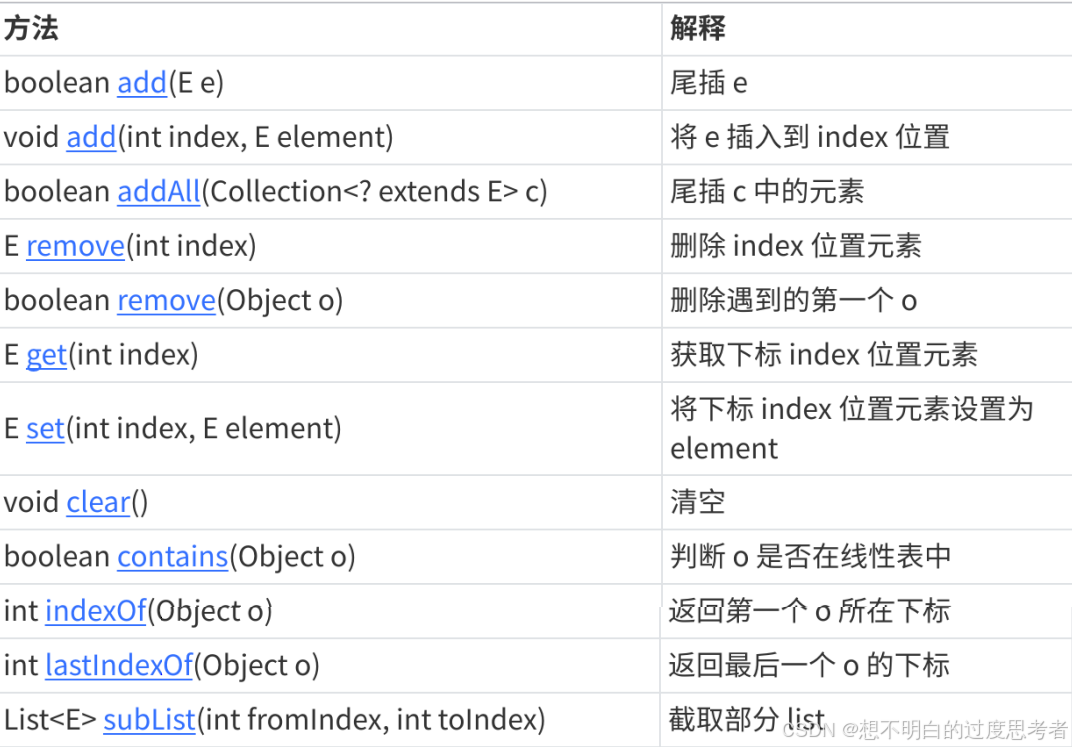
4.3 遍历方式
// 1. for-each循环for (int num : list) { System.out.print(num + " ");}
// 2. 迭代器Iterator<Integer> it = list.iterator();while (it.hasNext()) { System.out.print(it.next() + " ");}
// 3. 反向迭代器Iterator<Integer> rit = list.descendingIterator();while (rit.hasNext()) { System.out.print(rit.next() + " ");}🧩 5. 经典链表OJ题解析
5.1 反转链表
题目:反转一个单链表。
代码:
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { ListNode prev = null; ListNode cur = head; while (cur != null) { ListNode next = cur.next; cur.next = prev; prev = cur; cur = next; } return prev;}5.2 判断链表是否有环
快慢指针法:
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) { ListNode slow = head, fast = head; while (fast != null && fast.next != null) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; if (slow == fast) return true; } return false;}📊 6. ArrayList vs LinkedList
| 对比维度 | ArrayList | LinkedList |
|---|---|---|
| 底层结构 | 动态数组 | 双向链表 |
| 随机访问 | O(1) | O(n) |
| 头插/删效率 | O(n) | O(1) |
| 内存占用 | 连续空间,可能浪费 | 分散存储,无浪费 |
| 适用场景 | 频繁访问+少量修改 | 频繁插入/删除 |
选择建议:
- 需要快速随机访问?选
ArrayList! - 频繁在头部或中间插入/删除?选
LinkedList!
💡 7.记忆技巧
Iterable是根源,Collection分三派(List/Queue/Set),List有三各不同:数组实现ArrayList,链表实现LinkedList,线程安全Vector顶。
标记接口要记清:Serializable可序列,Cloneable能复制,RandomAccess随机快。🎯 总结
- 链表通过节点引用实现逻辑连续,适合频繁修改的场景。
- LinkedList在Java中基于双向链表实现,提供了高效的插入/删除操作。
- 理解链表的核心在于掌握指针操作和边界条件处理。
通过本文的学习,相信你对链表和LinkedList有了更深入的理解!快去LeetCode上挑战更多链表题目吧!
💬 互动话题:你在项目中用过LinkedList吗?遇到过哪些坑?欢迎评论区分享!
⛓️吃透LinkedList与链表的终极指南
https://mizuki.mysql.com/posts/datastructure/c/content/ 



